Cologne/Hanover, April 24, 2024 – Mobile robotics systems are being used in more and more work areas, in e-commerce warehouses as well as in modern restaurants. Conventional models on the market start at around 25,000 euros, while solutions with an integrated robot arm start at around 70,000 euros. However, widespread use in the market is often unaffordable for small and medium-sized enterprises due to the high prices. igus wants to change this with new low-cost robotics offerings and is presenting a series of low-cost mobile plastic robots at the Hannover Messe.
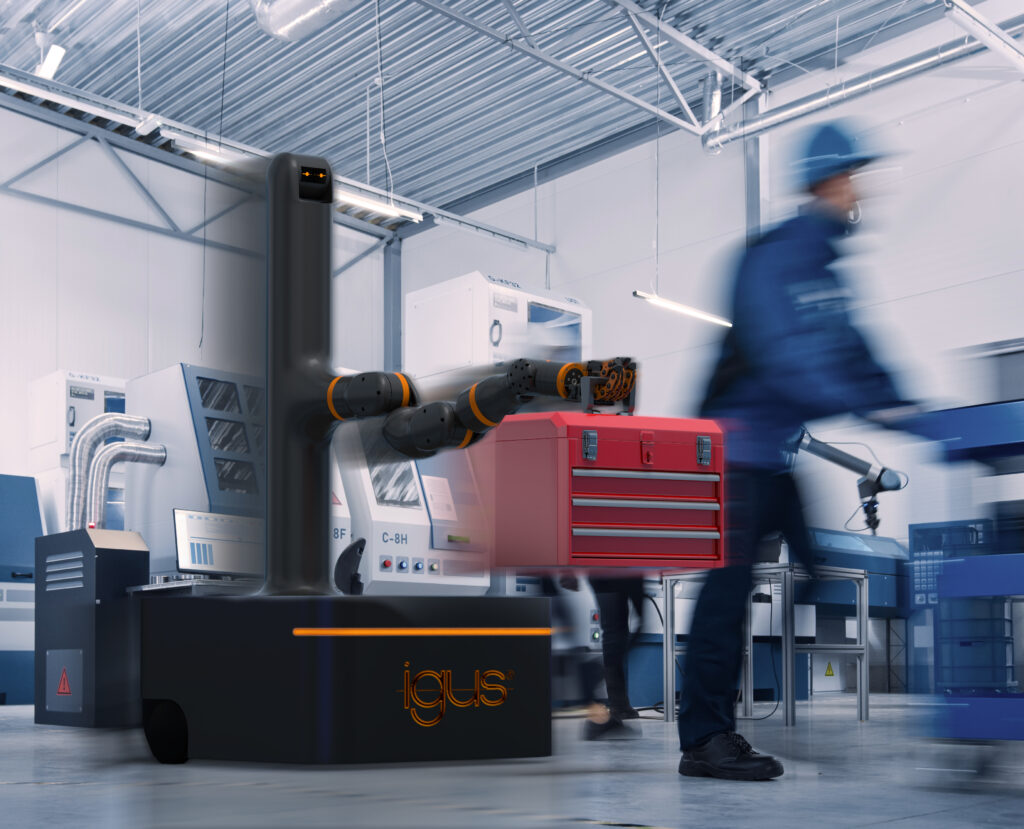
The market for Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) is booming: The global market for mobile robotics, including service robotics, is currently worth around 20.3 billion US dollars, and experts expect it to almost double by 2028. 1 Mobile robots are particularly common in intralogistics and industrial applications. And even in the catering industry or in hospitals, the smart helpers are increasingly making their rounds. This is also the case at motion plastics specialist igus: For four years now, the plastics experts have been successfully testing AGVs in-house – driverless racks that deliver mail and deliveries to offices, as well as mobile robots in production that move transports and stack-and-turn containers. The experience gained flows directly into the development of a new low-cost automation product line, the „ReBeL on Wheels“. Their goal: to pave the way for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to use cost-effective mobile robotics.
Mobile ReBeL solutions for education, logistics and service
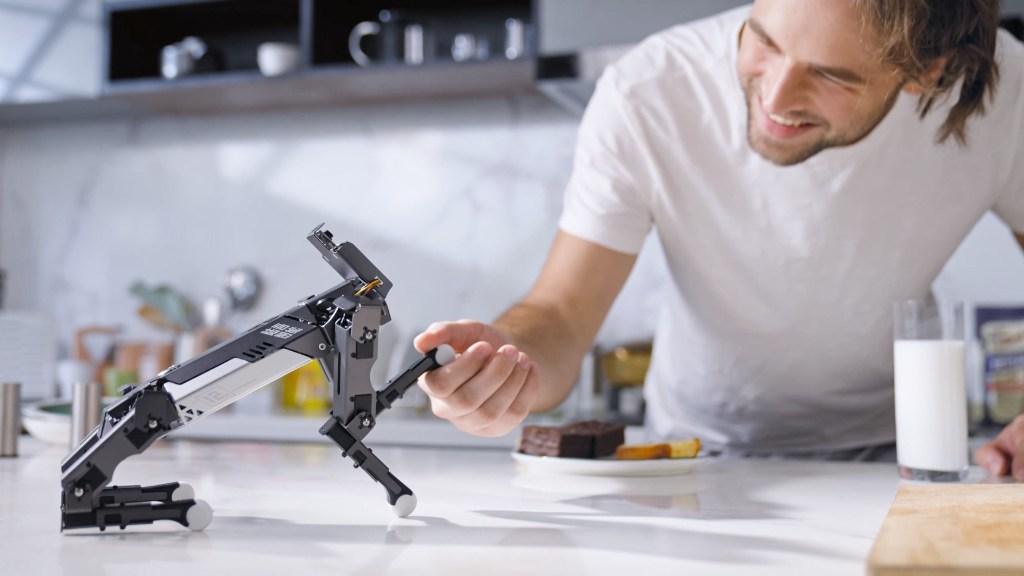
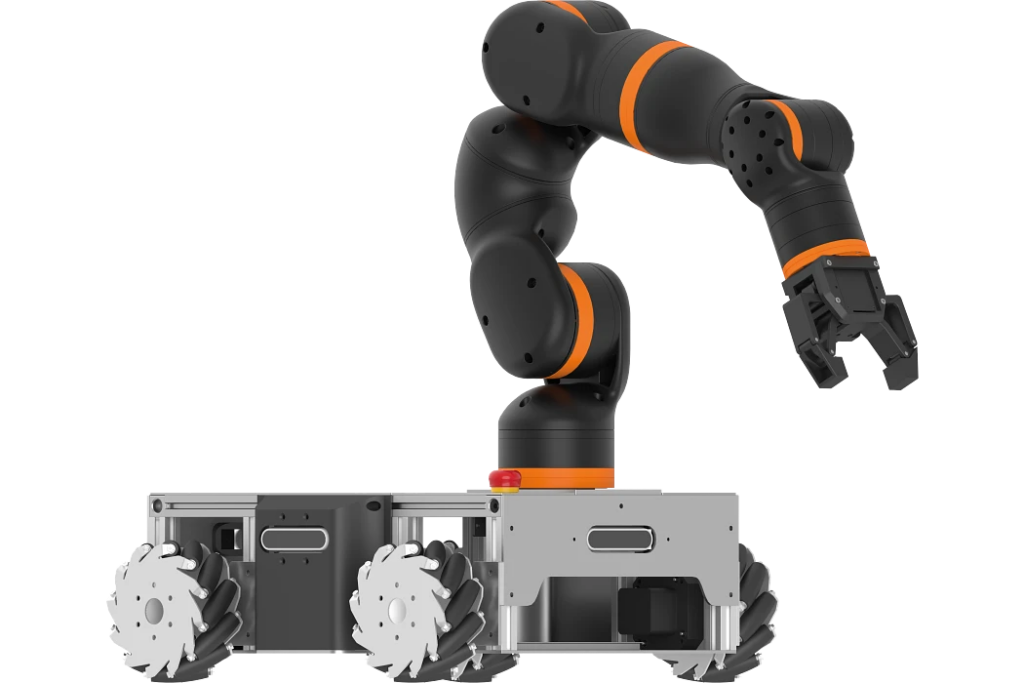
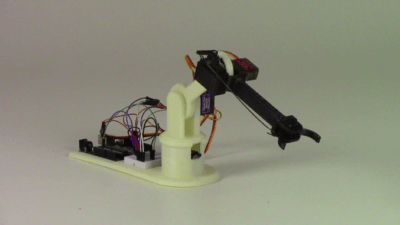
The basis of any mobile robotics system is the ReBeL. The use of plastic makes the robot particularly affordable at 4,970 euros and, with a dead weight of 8.2 kilograms, the lightest service robot with cobot function in its class. All mechanical components that make up the ReBeL are developed and manufactured by igus without exception. It has a load capacity of 2 kilograms and a reach of 664 millimetres. Various mobile systems are planned in which the ReBeL is centrally integrated: igus is launching an affordable version for the education sector for 14,699 euros – including the robot arm. The ReBeL EduMove equipped with a gripper serves as an autonomous learning platform for educational institutions thanks to open source. It has a modular design and can be flexibly expanded to include additional functions such as lidar, camera technology or slam algorithm. Another variant is an automated guided vehicle system for SMEs. It can carry up to 30 kilograms. With the optional ReBeL, simple A-to-B positioning can be made. It dispenses with expensive sensor technology and instead relies on 3D sensor technology developed in-house. The price is 17,999 euros. In addition, igus will be showcasing a study of a service robot at a low price in Hanover. The ReBeL Butler is suitable for simple but time-consuming pick-up and drop-off services, for example in the hotel and catering industry.
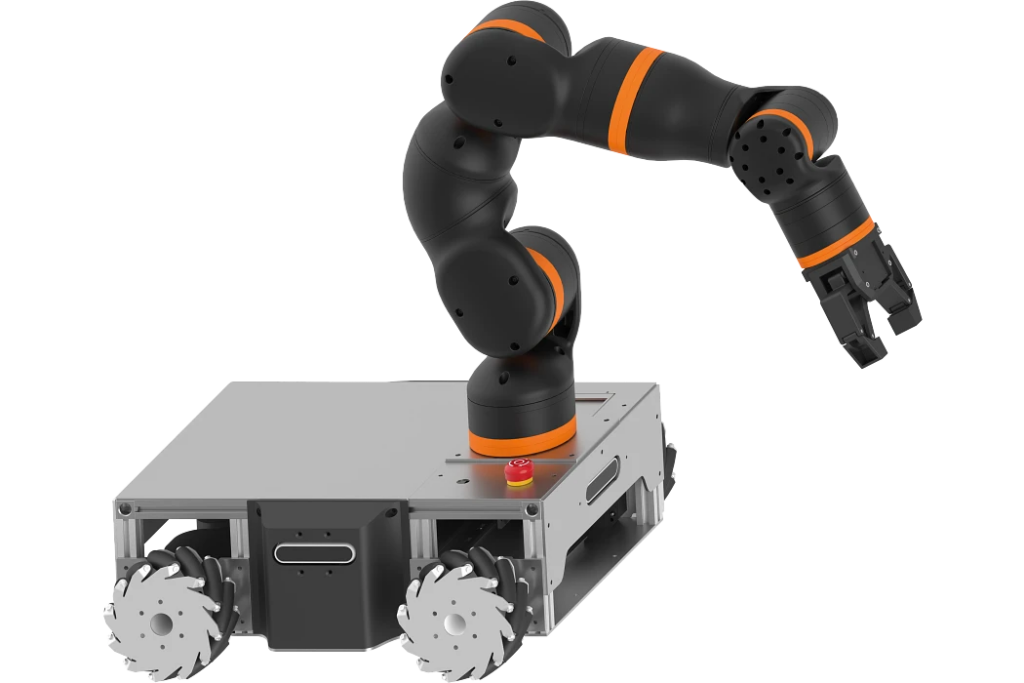
A lighthouse project on wheels
The goal of all these developments is the lighthouse project, a mobile robot with integrated HMI and vision that could even tidy up an office on its own. „With this project, we are pursuing a bottom-to-top strategy, in which certain components such as safety laser scanners are not included in the basic package in order to keep the price low,“ explains Alexander Mühlens, authorized signatory and head of the low-cost automation business unit at igus. „Nevertheless, it ensures that the solution can be retrofitted for industrial requirements.“ Among other things, igus is presenting an affordable gripper with a large stroke and travel this year, which offers a high degree of flexibility when gripping different geometries. Alexander Mühlens: „The areas of application for this targeted low-cost AMR are extremely diverse and go far beyond simple transport tasks. They encompass a huge range of applications in various areas of life, such as cleaning tasks or serving coffee directly at the workplace.“